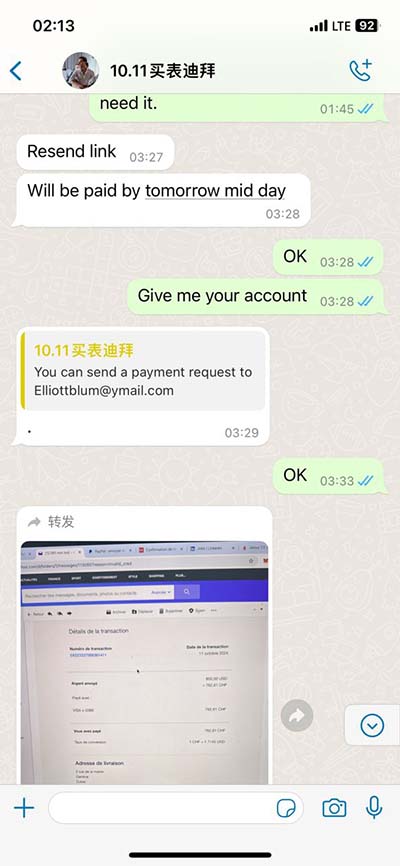
plot 2-d chanel lcoation eeglab | eeglab channel signal plot 2-d chanel lcoation eeglab Where are the EEG properties stored in EEGLAB’s EEG structure? How to work with the data array, events, channel coordinates, and ICA related fields. Objectives. Learn to interact with all . US. Rolex Explorer II. 1972 Rolex Explorer 2 Orange Hand ref. 1655 MK1 Dial Cream Patina. $ 26,000. + $100 for shipping. US. Rolex Explorer II. Steve McQueen 1655 .
0 · eeglab edit channel locations
1 · eeglab channels list
2 · eeglab channel signal
3 · eeglab channel names
4 · eeglab channel coordinates
5 · eeglab c channels
6 · eeglab c channel locations
7 · eeglab biosemi channel names
$6,493.00
EEGLAB allows plotting grand-average ERPs, spectra, ERPimage, and ERSP/ITCs. In this section of the tutorial, we will see how to pre-compute measures, how to plot them, and how to .
Plot data. Now that the data is clean, it is time to calculate behaviorally relevant EEG derived measures. This series of tutorials guides you to plot ERPs, spectra, ERP-images, and time .
dior sauvage recensie
To plot EEG scalp maps in either 2-D or 3-D format, or to estimate source locations for data components, an EEGLAB dataset must contain information about the .Table of Contents. I. Data Analysis Tutorial I.11.1. Decomposing channel data................................69 I.11.2. Computing .
Where are the EEG properties stored in EEGLAB’s EEG structure? How to work with the data array, events, channel coordinates, and ICA related fields. Objectives. Learn to interact with all . The 2D channel layout is a representation of the channel positions, together with the outline of the head or other anatomical features, that allows data to be plotted in a .3 levels of functions. Administrative functions: handle EEG and ALLEEG structures. eeglab(), eeg_checkset(), pop_delset(), . Pop functions: interactive functions using EEG structure. .
We have developed a toolbox and graphic user interface, EEGLAB, running under the crossplatform MATLAB environment (The Mathworks, Inc.) for processing collections of .
Plot Channel Spectra and Maps. To plot the channel spectra and associated topographical maps, select Plot → Channel spectra and maps. This will pop up the pop_spectopo.m window .To visualize the 2-D locations of the channels, press Plot 2-D above the Read Locations button. Else, during an EEGLAB session, you may refer to a plot showing the channel locations by selecting Plot → Channel location → By name. Either command pops up a .
EEGLAB allows plotting grand-average ERPs, spectra, ERPimage, and ERSP/ITCs. In this section of the tutorial, we will see how to pre-compute measures, how to plot them, and how to modify plotting parameters. Table of contents. Load the sample EEGLAB STUDY set. Precomputing and plotting ERPs.Plot data. Now that the data is clean, it is time to calculate behaviorally relevant EEG derived measures. This series of tutorials guides you to plot ERPs, spectra, ERP-images, and time-frequency decompositions for EEG data and ICA-resolved EEG sources. To plot EEG scalp maps in either 2-D or 3-D format, or to estimate source locations for data components, an EEGLAB dataset must contain information about the locations of the recording electrodes. KEY STEP 5: Load the channel locations. To load or edit channel location information contained in a dataset, select Edit > Channel locations.
Table of Contents. I. Data Analysis Tutorial I.11.1. Decomposing channel data................................69 I.11.2. Computing component time/frequency transforms...................71 I.11.3.Where are the EEG properties stored in EEGLAB’s EEG structure? How to work with the data array, events, channel coordinates, and ICA related fields. Objectives. Learn to interact with all the aspects of an EEG data file in EEGLAB. Establish a global view . The 2D channel layout is a representation of the channel positions, together with the outline of the head or other anatomical features, that allows data to be plotted in a topographically consistent manner on a 2D computer screen (or piece of paper).
3 levels of functions. Administrative functions: handle EEG and ALLEEG structures. eeglab(), eeg_checkset(), pop_delset(), . Pop functions: interactive functions using EEG structure. pop_erpimage(), pop_topoplot(), pop_envtopo(), . Signal . We have developed a toolbox and graphic user interface, EEGLAB, running under the crossplatform MATLAB environment (The Mathworks, Inc.) for processing collections of single-trial and/or averaged EEG data of any number of channels.Plot Channel Spectra and Maps. To plot the channel spectra and associated topographical maps, select Plot → Channel spectra and maps. This will pop up the pop_spectopo.m window (below). Leave the default settings and press Ok. The function should return a spectopo.m plot (below).To visualize the 2-D locations of the channels, press Plot 2-D above the Read Locations button. Else, during an EEGLAB session, you may refer to a plot showing the channel locations by selecting Plot → Channel location → By name. Either command pops up a .
EEGLAB allows plotting grand-average ERPs, spectra, ERPimage, and ERSP/ITCs. In this section of the tutorial, we will see how to pre-compute measures, how to plot them, and how to modify plotting parameters. Table of contents. Load the sample EEGLAB STUDY set. Precomputing and plotting ERPs.Plot data. Now that the data is clean, it is time to calculate behaviorally relevant EEG derived measures. This series of tutorials guides you to plot ERPs, spectra, ERP-images, and time-frequency decompositions for EEG data and ICA-resolved EEG sources. To plot EEG scalp maps in either 2-D or 3-D format, or to estimate source locations for data components, an EEGLAB dataset must contain information about the locations of the recording electrodes. KEY STEP 5: Load the channel locations. To load or edit channel location information contained in a dataset, select Edit > Channel locations.
eeglab edit channel locations
Table of Contents. I. Data Analysis Tutorial I.11.1. Decomposing channel data................................69 I.11.2. Computing component time/frequency transforms...................71 I.11.3.
Where are the EEG properties stored in EEGLAB’s EEG structure? How to work with the data array, events, channel coordinates, and ICA related fields. Objectives. Learn to interact with all the aspects of an EEG data file in EEGLAB. Establish a global view . The 2D channel layout is a representation of the channel positions, together with the outline of the head or other anatomical features, that allows data to be plotted in a topographically consistent manner on a 2D computer screen (or piece of paper).3 levels of functions. Administrative functions: handle EEG and ALLEEG structures. eeglab(), eeg_checkset(), pop_delset(), . Pop functions: interactive functions using EEG structure. pop_erpimage(), pop_topoplot(), pop_envtopo(), . Signal . We have developed a toolbox and graphic user interface, EEGLAB, running under the crossplatform MATLAB environment (The Mathworks, Inc.) for processing collections of single-trial and/or averaged EEG data of any number of channels.
dior schoenen grijs
dior nagellak opal 001
eeglab channels list
$3,685.00
plot 2-d chanel lcoation eeglab|eeglab channel signal